Latest News Regarding Your Health
Loading…
Latest Exercise & Fitness News TUESDAY, Feb. 25, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Do you ride your bike to work? If you don’t, maybe you should. Why? People who commute by bicycle are at lower risk of dying early, a new study from New Zealand finds. Researchers from the University of Otago, Wellington, the University of Melbourne and the University of Auckland found that those who cycled to work had a 13% reduction in death during the study period. Lead researcher Dr. Caroline Shaw attributes this mortality reduction to the health benefits of physical activity that aren’t typically seen from walking or taking public transportation. For the study, Shaw and her team analyzed data from 3.5 million New Zealanders. “We studied 80% of the working-age population of New Zealand over a 15-year period, so it is highly representative,” Shaw said in a University of Otago news release. Only 3% of those studied cycled to work. In comparison, over 80% of people in New Zealand traveled to work by car. “There were gender differences in mode of travel to work, with 2% of women cycling compared with 4% of men, but more women walking or jogging (7%) compared with men (5%),” Shaw […]
Latest Digestion News By Amy NortonHealthDay Reporter TUESDAY, Feb. 25, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Common heartburn meds may foster the growth of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the gut, a new research review suggests. In an analysis of 12 past studies, researchers found that, overall, the evidence supports a link: People who use acid-suppressing medications — particularly proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) — are more likely than nonusers to harbor antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the gut. The findings do not prove that PPIs — which include popular brands such as Prilosec (omeprazole), Prevacid (lansoprazole) and Nexium (esomeprazole) — are the cause, experts said. But they are the latest to raise safety questions about the top-selling prescription and over-the-counter medicines. In recent years, studies have linked long-term PPI use to increased risks of heart and kidney disease, stomach cancer and certain infections — as well as deficiencies in calcium, magnesium and vitamin B12. That said, PPIs are generally safe to use, according to Dr. Todd Lee, an associate professor of medicine at McGill University in Montreal. But, he said, it’s known that doctors overprescribe the drugs and that many people take them longer than necessary. So any safety concerns underscore the importance of using PPIs […]
Latest Diet & Weight Management News By Serena GordonHealthDay Reporter WEDNESDAY, Feb. 26, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Starting the day with a big breakfast and keeping dinner light may help you burn more calories and keep you trimmer, new research suggests. Eating this way may also keep your blood sugar levels from going too high, the small study found. “Extensive breakfasting should be preferred over large dinner meals,” said study lead author Juliane Richter, of the University of Lubeck’s Center of Brain, Behavior and Metabolism in Germany. “This recommendation can be applied to healthy people to prevent metabolic diseases [such as diabetes], as well as to patients with overweight and obesity to reduce body weight,” she added. How could eating breakfast improve your weight and blood sugar levels? Richter said the reason isn’t clear yet and more study is needed. But it appears that digestion and metabolism keep pace with the body’s internal clock, she said. Another reason may be that if you don’t eat enough earlier, you’ll be more hungry throughout the day, Richter said. That could lead to overeating, or to eating the wrong kinds of foods later in the day. She also noted more calories are burned […]
Latest Cold and Flu News WEDNESDAY, Feb. 26, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Anywhere from 4% to 10% of adults have troublesome chronic cough, defined as an unexplained cough lasting more than eight weeks. But a new drug may offer some long-sought relief. Reporting Feb. 25 in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, British researchers said the experimental drug, called gefapixant, blocks a cellular receptor that’s key to the cough reflex. “Many patients with a chronic cough are driven to seek treatment because of the significant negative impact it can have on their quality of life, but at the moment physicians are unable to help,” noted study leader Jacky Smith, a professor at the University of Manchester, in England. This “is the first study to report a treatment that is safe and effective over the longer term,” Smith said in a journal news release. She added that “phase 3 trials are already underway with an even larger group of people and over a longer time frame.” The trial was funded by the drug’s maker, Merck, and involved 253 American and British participants. All had suffered from an unexplained or untreatable cough that had lasted for an average of almost 15 years. Three-quarters were […]
Latest Chronic Pain News TUESDAY, Feb. 25, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Here’s a good reason to put your electronic devices down whenever you can: Experts say that using them incorrectly or too often can put you at risk for a range of injuries. “When people position their hand, arm or neck in uncomfortable positions for a prolonged period of time, it can lead to strains and overuse injuries,” said Dr. Michael Darowish, an orthopedic surgeon at Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center. Overuse, nerve and neck injuries are the three common types of problems, he said. Nearly all types of overuse injuries such as “swiper’s thumb” and “iPad hand” are a type of tendonitis. “Often, we find it’s De Quervain’s tenosynovitis, an inflammation of the tendons that abduct the thumb,” Darowish said in a Penn State news release. “Pregnant women and parents who often lift their young kids are prone to it, too.” Tendonitis also may occur in the fingers or wrists. Pain while texting, aching and soreness are mild symptoms. Rest, anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen, and changes to activity can ease the pain. Severe cases may require cortisone injections, bracing or even surgery to calm the […]
Latest Cancer News WEDNESDAY, Feb. 26, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Female firefighters are exposed to chemicals that may be linked with breast and other types of cancer, researchers say. Compared to women working in offices, female firefighters in San Francisco are exposed to higher levels of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). These chemicals are used in firefighting foam and uniforms, grease- and water-resistant coatings and in fabrics, furniture and food packaging. PFAS have been linked to a number of cancers and are known to interfere with breast development as well as immune and endocrine function, according to the study published Feb. 26 in the journal Environmental Science and Technology. It’s one of the first published from the Women Firefighter Biomonitoring Collaborative, a long-term investigation into chemical exposure among female firefighters. “Women firefighters actually raised concern about what they have perceived as elevated rates of breast cancer among their cohort in San Francisco,” said study lead author Jessica Trowbridge, a doctoral student in the School of Public Health at the University of California, Berkeley. “As a team, we decided to conduct an exposure study looking at chemicals that are potential breast carcinogens,” Trowbridge said in a university news release. Studies looking […]
Latest Digestion News By Amy NortonHealthDay Reporter MONDAY, Feb. 24, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Doctors thought they had a fairly common scenario in front of them: A patient with advanced liver disease who needed help for her alcohol abuse. Then they discovered her own bladder was making the alcohol. The doctors, at the University of Pittsburgh, say it’s a previously unrecognized variant of so-called auto-brewery syndrome. ABS, which has been reported sporadically over the years, occurs when yeast builds up in the gut and converts sugar from food into alcohol. “Traditional” ABS causes blood alcohol to spike, along with symptoms like dizziness, disorientation, coordination problems and mood changes. In contrast, this new variant — what the Pitt team terms urinary ABS — does not affect blood alcohol. Instead, yeast in the bladder produces alcohol in the urine. The patient in this case, who was 61 and had liver cirrhosis, did not show symptoms of intoxication. But her urine tests repeatedly came back positive for alcohol, which meant she could not be placed on the waitlist for a donor liver. Doctors at her initial transplant center told her she would have to undergo treatment for alcohol abuse — a problem she […]
Latest Diet & Weight Management News By Steven ReinbergHealthDay Reporter MONDAY, Feb. 24, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Chicago’s brief and now-defunct soda tax did cut the consumption of sugar-sweetened drinks, a new study finds, along with raising funds for public health initiatives. From August to November 2017, when the tax was in effect, the volume of soda sold in Cook County dropped 21% and the tax raised nearly $62 million, nearly $17 million of which went to a county health fund. “The evidence suggests that taxes on sweetened beverages may be an effective policy tool for reducing sweetened beverage consumption,” said lead researcher Lisa Powell. She’s director of health policy and administration at the University of Illinois at Chicago’s School of Public Health. “The evidence also shows that households will undertake tax avoidance strategies, such as cross-border shopping, which will dampen the impact of the tax,” Powell said. The Cook County levy was 1 cent per ounce on sodas and other sugar-sweetened drinks. After two months, pressure from the public and extensive lobbying by the American Beverage Association forced the Cook County Board of Commissioners to rescind the tax, the Washington Post reported. Samantha Heller, a senior clinical nutritionist at […]
Latest Travel Health News MONDAY, Feb. 24, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Buckle up and get ready for take-off: Flying has never been safer, an expert says. Despite recent high-profile crashes of Boeing aircraft, the news on flight safety is good: Airline passenger deaths have dropped sharply in recent decades around the world, according to Arnold Barnett, a professor of management at MIT. “The worldwide risk of being killed had been dropping by a factor of two every decade,” Barnett said in an MIT news release. “Not only has that continued in the last decade, the [latest] improvement is closer to a factor of three. The pace of improvement has not slackened at all even as flying has gotten ever safer and further gains become harder to achieve,” he added. “That is really quite impressive and is important for people to bear in mind.” He found that commercial flights for the decade 2008-2017 resulted in one death per 7.9 million passenger boardings, compared to one death per 2.7 million boardings during 1998-2007. The rate was higher during 1988-1997, with one death per 1.3 million boardings. Looking further back, the researchers found the rate was one death per 750,000 boardings from 1978-1987, […]
Latest Sexual Health News By Adam Townsend on 02/25/2020 8:32 PM Source: MedicineNet Health News Even as the latest government statistics show record numbers of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) throughout the U.S., a major health poll shows most people are oblivious. As the U.S. Centers for Disease Control works to tamp down spikes in STD rates through screening initiatives and other measures, a February survey by the Kaiser Family Foundation shows that two thirds of adult Americans don’t even realize STDs are a growing problem. The CDC numbers are grim. Rates for many STDs rose from 2017 to 2018, but one of the most dramatic fluctuations is in the total cases of chlamydia, gonorrhea and syphilis — combined, the number represents an all-time high in U.S. history, according to the agency. In 2018 – the most recent stats available – 2.5 million had an active sexually transmitted infection. This includes almost 1.8 million with chlamydia, nearly 600,000 with gonorrhea and 115,000 cases of syphilis, both primary and congenital (passed from infected mother to baby). In fact, the number of infant deaths from congenital syphilis rose 22% in the U.S. from 2017 to 2018, from 77 to 94 deaths. Total congenital syphilis cases […]
Latest Senior Health News By Dennis ThompsonHealthDay Reporter MONDAY, Feb. 24, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Americans may want to rethink the stereotype of the pot-loving teen: More U.S. seniors are using the drug now than ever before. The proportion of folks 65 and older who use pot stands at 4.2%, up from 2.4% in 2015, according to figures from the U.S. National Survey on Drug Use and Health. “The change from 2.4 up to 4.2, that’s a 75% increase,” said senior researcher Joseph Palamar, an associate professor of population health at New York University Langone Medical Center. “It didn’t double, but 75% is a pretty big increase, I think.” Emily Feinstein, executive vice president and chief operating officer at the Center on Addiction, reviewed the study and commented that the trend is “not surprising.” “First, older people are more likely to experience pain and other chronic conditions,” Feinstein said. “Secondly, marijuana has become increasingly available and acceptable within society. Together, these two factors are probably driving this trend.” But Palamar doesn’t think the wave of marijuana legalization sweeping the nation has prompted Grandma and Grandpa to give weed a try, either to ease aches and pains or have a pleasant […]
Latest Prevention & Wellness News MONDAY, Feb. 24, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Americans don’t seem to care about the race or sex of emergency room doctors, a new study shows. Participants were asked to rate their satisfaction with a simulated ER visit and the scores were the same whether their doctor was white or black, or a man or a woman. “We were really surprised that even after looking at these data in many different ways, we did not see evidence of racial or gender bias affecting patient satisfaction or confidence. This is not to say that people are bias-free, but it did not appear to enter into their ratings of care in surveys,” said lead author Dr. Rachel Solnick, a fellow in the clinical scholars program at the University of Michigan, in Ann Arbor. “This is good news, with a grain of salt,” she added in a university news release. The findings don’t mean emergency doctors won’t ever have to deal with patients who express bias against them because of race, gender, age or other factors, Solnick added. The research was inspired by her own experience with bias as an emergency medicine resident. Assessing patient bias is important because […]
Latest Neurology News By Serena GordonHealthDay Reporter TUESDAY, Feb. 25, 2020 (HealthDay News) — By the time he was 7 months old, John Michael Crawford had been diagnosed with a rare genetic disorder called tuberous sclerosis, associated with a high risk of developmental delays, including autism. Early intervention programs are believed to help reduce that risk, but these time- and labor-intensive therapies often aren’t available in areas of the United States that aren’t close to large medical centers. The Crawfords, from Benton, Ark., live in such an area. “There are plenty of families who live in places without access to specialists. It’s overwhelming when you get the diagnosis, especially when you can’t find specialists that can answer questions and teach you,” said John Michael’s father, Brandon Crawford. An ongoing trial for a program developed at University of California, Los Angeles seeks to change that with the novel use of technology and developmental intervention therapy for families of children with a high risk of autism that live in rural areas. Dr. Shafali Jeste, an associate professor at the UCLA Center for Autism Research and Treatment, said, “We’re very proficient at making the diagnosis of autism, but families often can’t get access […]
Latest Skin News SUNDAY, Feb. 23, 2020 (HealthDay News) — People sometimes refer to menopause as “the change of life,” but many women are surprised that one of the things that changes is their skin, an expert says. “Although fluctuating hormones during menopause can result in a number of skin changes, these don’t need to be disruptive to daily life,” said New York City dermatologist Dr. Diane Berson. “With the right care, women can continue to have healthy, blemish-free skin during midlife and beyond.” During menopause, declining estrogen levels result in dryness and itching. Wash with a mild cleanser, as regular soap may be too drying, Berson suggested in an American Academy of Dermatology news release. After bathing or showering and throughout the day, apply a moisturizer with hyaluronic acid or glycerin. To help soothe itchy skin, apply a cool, wet compress, then a moisturizer. Another way to relieve itchy skin is to take a colloidal oatmeal bath. Colloidal oatmeal is available in most drug and beauty stores. Use warm, not hot, water and pat your skin dry — instead of rubbing — to avoid further irritation, Berson advised. If fluctuating hormones leave you with acne, wash with a cleanser […]
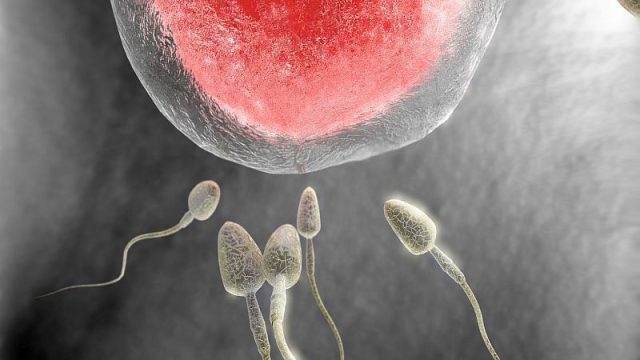
Latest Sexual Health News By Steven ReinbergHealthDay Reporter FRIDAY, Feb. 21, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Listen up, guys: A healthy diet is good for your brain and heart, and also your sperm, new research suggests. In a study of more than 2,900 Danish men, median age 19, those whose diet was rich in fish, chicken, vegetables, fruit and water had higher sperm counts than those who ate a “Western” diet rich in pizza, French fries, processed and red meats, snacks, refined grains, sugary beverages and sweets, researchers found. “Because following a generally healthy diet pattern is a modifiable behavior, our results suggest the possibility of using dietary intervention as a possible approach to improve sperm quality of men in reproductive age,” said lead study author Feiby Nassan. She’s a postdoctoral research associate at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, in Boston. Sperm count can affect fertility because the lower the count, the lower the chance of getting a partner pregnant. “It may be useful for men’s fertility to follow a generally healthy diet,” Nassan said. For the study, her team compared sperm counts among men who ate a healthy diet; a Western diet; a Danish diet rich in cold […]
Latest Senior Health News FRIDAY, Feb. 21, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Dietitian-led intensive behavioral therapy may help obese seniors lose weight, a new study suggests. Intensive behavioral therapy for obesity (IBTO) features individualized counseling sessions to help people change their eating and exercise habits, CNN reported. The East Carolina University study of nearly 2,100 obese women, aged 65 and older, found that after three years, those who received IBTO lost an average of nearly three pounds, while those who didn’t receive IBTO gained an average of half a pound. Those who received IBTO also had an average A1C decline of nearly 0.2, which previous research suggests is associated with an up to 10% decrease in death risk, CNN reported. A1C is a blood test for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. IBTO is provided and reimbursed for Medicare B recipients, who would be 65 or older, the study authors noted. Copyright © 2019 HealthDay. All rights reserved. SLIDESHOW How to Lose Weight Without Dieting: 24 Fast Facts See Slideshow
Latest Prevention & Wellness News SATURDAY, Feb. 22, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Hitting the slopes or the skating rink as the winter of 2020 winds down? Don’t let an accident or injury spoil your fun. “Winter sports and recreational activities have great health and cardiovascular benefits,” said Dr. Joseph Bosco, vice president of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS). “However, it’s important not to underestimate the risks that cold weather can bring.” He noted that hospitals and health care clinics see a surge of bone and joint injuries during the winter months and many could be prevented with the right preparation. Sprains, strains, dislocations, fractures and more traumatic injuries can happen to anyone. Here, Bosco and the AAOS offer suggestions on how to protect yourself: Be prepared: Before you tackle a winter sport, make sure your muscles are warmed up and in good condition. Cold muscles, tendons and ligaments are more prone to injury. Make sure to have water and other supplies on standby. Wear appropriate gear: Well-fitting protective equipment like goggles, helmets, gloves and padding is crucial. Your clothes should be layered, light, loose and wind-resistant. Footwear should be warm, provide ankle support and keep your feet dry. […]
Latest Neurology News FRIDAY, Feb. 21, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Canadian doctors who conducted the first robotic surgery to treat a brain aneurysm say the approach could boost the availability and precision of lifesaving stroke care. Use of the technology could also be a first step toward remote robotic surgery for stroke and other conditions affecting brain blood vessels. “In the future, perhaps, a patient could end up in a small center somewhere, and the staff there could put the patient into the appropriate suite where the procedure can be done,” explained American Heart Association president-elect Dr. Mitchell Elkind. “And then, an expert at another site, perhaps hundreds or even thousands of miles away, could perform the procedure remotely. It’s really like science fiction stuff. It sounds really exciting and it has great potential.” Elkind wasn’t involved in the new report, which was led by Dr. Vitor Mendes Pereira, a neurosurgeon and neuroradiologist at the Toronto Western Hospital. His team presented their findings Friday at the International Stroke Conference, in Los Angeles. As the Canadian doctors explained, robotic technology is already used in many surgeries, including cardiac procedures. But it has not yet been tried in delicate neurovascular surgeries — […]
Latest Mental Health News By Dennis ThompsonHealthDay Reporter FRIDAY, Feb. 21, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Americans are drinking themselves to death at ever-increasing rates, with women in particular hitting the bottle hard, a new study shows. The rate of alcohol-induced deaths among women increased between 3.1% and 3.6% a year from 2000 to 2016, while deaths among men increased 1.4% to 1.8% each year, according to the findings. What’s worse, the rates have accelerated in recent years — the average annual increase for women was 7.1% between 2013 and 2016, and for men it was 4.2% between 2012 and 2016. “The opioid crisis has generated the most attention in the media, and certainly in Washington as well, but this study demonstrates that America has had a serious alcohol problem for decades,” said Dr. Timothy Brennan, director of the Addiction Institute of Mount Sinai West and Mount Sinai St. Luke’s in New York City. “This study really underlines the ongoing public health menace of alcohol use disorder and risky and dangerous drinking,” added Brennan, who was not involved with the study. This is just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to drink-related fatalities. The deaths documented here were solely […]
Latest Infectious Disease News MONDAY, Feb. 24, 2020 (HealthDay News) — A coronavirus pandemic looked ever more likely on Monday as multiple countries around the world raced to stem outbreaks of “untraceable” cases of the virus. Clusters of cases arising in South Korea, Italy and Iran with no clear ties to outbreak’s epicenter in China have heightened concerns about local, self-sustaining epidemics and a global pandemic. In a pandemic, outbreaks occur on more than one continent. As of Monday, there were more than 79,000 cases of COVID-19 and 2,600 deaths globally. “We are worried about the situation in the Islamic Republic of Iran and in Italy,” Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, director of the World Health Organization, said Monday. “It is an incredible time. Less than two months ago, the coronavirus was completely unknown to us,” Ghebreyesus said. “The past few weeks have demonstrated just how quickly a new virus can spread around the world and cause widespread fear and disruption.” As reported Monday by Associated Press, the list of countries with burgeoning case counts includes: South Korea. Total cases of COVID-19 have risen from just 28 last week to 833 by Monday. Seven people have died. South Korea now has the […]
Latest Infectious Disease News SATURDAY, Feb. 22, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Outbreaks of “untraceable” cases of coronavirus in multiple countries around the world are raising the real possibility of a pandemic, public health experts say. Clusters of cases arising in South Korea, Iran, Italy and Canada with no clear ties to the outbreak’s epicenter in China have boosted concerns about local, self-sustaining epidemics and a global pandemic. As reported Saturday by CNN, the list of countries with burgeoning case counts includes: South Korea. Total cases of COVID-19 have risen from just 28 last week to 433 by Saturday, with a jump of 229 cases in just over the past 24 hours. Two people have died. Most cases are centered in the southern city of Daegu, and more than half are concentrated among members of the Shingeongji religious group. “We have secured a list of about 9,300 members of the relevant religious group, and we are preemptively enforcing self-isolation and facility isolation,” Kim Gang-lip, South Korea’s vice minister of health, said at a press briefing. Iran. So far, Iranian officials say 28 cases have been identified and five people have died — bringing the global death toll from coronavirus outside Asia […]
Latest Infectious Disease News By E.J. MundellHealthDay Reporter FRIDAY, Feb. 21, 2020 (HealthDay News) — A report from doctors battling China’s coronavirus outbreak raises concern that people who have no symptoms and initially test negative on medical tests might still harbor and spread the COVID-19 virus. The case involves an asymptomatic 20-year-old woman who appears to have spread the illness to five relatives who later became ill. If similar reports are found elsewhere, “the prevention of COVID-19 infection would prove challenging,” warned researchers led by Dr. Meiyun Wang of Henan Provincial People’s Hospital in Zhengzhou, China. While the rate of new cases in China appear to be slowing, outbreaks in countries such as South Korea and Iran have experts worried that COVID-19 could go global. As of Friday, a total of more than 75,000 cases and 2,236 deaths were reported in mainland China. For many infectious respiratory illnesses, people have to be symptomatic to transmit the infection to others. But the new report suggests that might not always be the case for COVID-19. As Wang’s team explained, five members of a family in the Chinese city of Anyang came down with coronavirus about 10 days after meeting up with a […]
Latest High Blood Pressure News FRIDAY, Feb. 21, 2020 (American Heart Association News) — Nearly two-thirds of people who survive an often-deadly type of stroke caused by bleeding in the brain continue to experience high blood pressure because they aren’t taking enough medication, new research shows. The preliminary study, presented this week at the American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference in Los Angeles, found most people who survive an intracerebral hemorrhage need three or more medications to control severe hypertension afterward. “If they don’t achieve control, the risk of a recurrent stroke is three to four times higher,” said lead researcher Dr. Kay-Cheong Teo, of the University of Hong Kong’s department of medicine. His team included researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. The study of 1,172 bleeding stroke survivors from Boston and Hong Kong found 64.3% of those in Boston and 32.7% in Hong Kong continued to experience high blood pressure, also called hypertension, six months after their strokes, despite treatment. About a third of the Boston stroke survivors and nearly as many in Hong Kong, 29.7%, experienced hypertension that was resistant to medication. But the balance – 66.5% in Boston and 70.3% in Hong Kong – were not […]
Latest Heart News MONDAY, Feb. 24, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Want to avoid a stroke? Reach for fruits and veggies, new research suggests. The new European study of more than 418,000 people found that what you eat can influence your risk for different types of stroke. “The most important finding is that higher consumption of both dietary fiber and fruit and vegetables was strongly associated with lower risks of ischemic stroke,” said study lead author Tammy Tong. She’s a nutritional epidemiologist at the University of Oxford, in England. This study involved patients from nine European countries, and it investigated how diet affects both ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. Ischemic strokes — about 85% of cases — occur due to blockages in a vessel, while hemorrhagic strokes involve bleeds from blood vessels. People who consumed greater amounts of fruit, vegetables, fiber, milk, cheese or yogurt had a lower risk of ischemic stroke, Tong’s group found, but there was no significant association with hemorrhagic stroke. Eating more eggs was associated with a higher risk of hemorrhagic stroke, but not with ischemic stroke. The total amount of fiber (including fiber from fruit, vegetables, cereal, legumes, nuts and seeds) was associated with the greatest reduction […]
Latest Heart News MONDAY, Feb. 24, 2020 (HealthDay News) — A specific collection of gut bacteria may be a culprit in the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), a new study shows. PAH is a chronic disease marked by the narrowing of arteries that supply blood to the lungs. With constant high blood pressure in these arteries, the right side of the heart is forced to work harder, which can result in right-sided heart failure. Symptoms of PAH include shortness of breath, heart palpitations and fatigue. Microbiota, bacteria found in everyone’s gut, aid in digestion. The study showed that having a particular microbiota profile predicted PAH with 83% accuracy. “We showed for the first time that specific bacteria in the gut are present in people with PAH. While current PAH treatments focus on the lungs, looking at the lung/gut axis could open the door to new therapies centered in the digestive system,” said lead study author Mohan Raizada. He is a distinguished professor in the department of physiology and functional genomics at the University of Florida College of Medicine in Gainesville. Stool samples from 18 PAH patients and 12 people without cardiopulmonary disease history were collected for the study. The […]
Latest Heart News FRIDAY, Feb. 21, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Ambulances outfitted as “mobile stroke treatment units” provide faster treatment and reduce patients’ risk of severe disability and death, German researchers report. The new study examined the use of three mobile stroke units in Berlin. Each unit is staffed with emergency medicine neurologists and has a CT scanner and lab on board that enables treatment at the scene. Treatment may include clot-busting drugs to restore blood flow to the brain. Timing of this treatment is crucial because the clot-busting medication alteplase should be given within 4.5 hours of stroke symptoms. “Just waiting until the patient arrives at the hospital is not enough anymore,” said lead author Dr. Heinrich Audebert, a professor in the Center for Stroke Research at Charité Universitätsmedizin, in Berlin. The study included 749 patients (average age 73) who were treated by the mobile units, and 794 patients (average age 74) who received regular care in the hospital. Sixty percent of patients treated in a mobile stroke unit received the clot-busting drug, compared with 48% of patients who received conventional treatment in the hospital, the study found. When a mobile unit was dispatched, time to treatment was reduced […]
Latest Cholesterol News MONDAY, Feb. 24, 2020 (HealthDay News) — A new type of cholesterol-lowering drug that works differently than statins has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Esperion Therapeutics Inc.’s Nexletol will provide an alternative for people who can’t tolerate or don’t fully respond to statins such as Lipitor and Crestor, the Associated Press reported. Nexletol is a daily pill approved for people with a genetic predisposition for high cholesterol and for heart disease patients who need to further reduce their bad cholesterol. The drug is to be taken at the highest dose patients can tolerate and used in conjunction with a healthy diet, according to the FDA. “This is a nice alternative” to statins, but statins will still be the first choice, Dr. Christie Ballantyne, Baylor College of Medicine’s cardiology chief, told the AP. He consults for Esperion and helped test Nexletol. Copyright © 2019 HealthDay. All rights reserved. SLIDESHOW Lower Your Cholesterol, Save Your Heart See Slideshow
Latest Cancer News “The dose makes the poison,” said Swiss doctor and chemist Paracelsus, meaning a substance is toxic only if it is present in the body in a high enough concentration. But now researchers at the University of Northern Colorado (UNC) believe small amounts of poisonous snake venom may one day help treat cancer. Researchers in the lab of UNC Professor of Biology Steve Mackessy, Ph.D., are studying venoms from several species of snakes looking for potential molecules that may have therapeutic properties. In a podcast discussing his work, Mackessy explains that when analyzing venoms he wonders: “Do they have compounds in them that are interesting, biologically? Interesting potentially therapeutically?” Mackessy and his team isolate compounds from snake venom and test them on human cancer cells cultured in the lab. Venoms from various snakes have different activity against cancer cells. For example, his group discovered that a toxin isolated from Indian snake venom had effects on a certain type of colon cancer cells in the lab, he said in the podcast. Mackessy further discussed how certain compounds from snake venom are capable of inducing programmed cell death, or apoptosis. One key to determining if a compound has therapeutic potential […]
Latest Cancer News FRIDAY, Feb. 21, 2020 (HealthDay News) — As rural hospitals and specialty care units close, a new study shows that some breast cancer patients are forced to travel long distances for their treatments. University of Minnesota researchers found that those living in rural parts of the United States travel three times as far as urban women for radiation therapy. The study, led by Ph.D. student Colleen Longacre, analyzed Medicare data from over 52,000 women diagnosed with breast cancer between 2004 and 2013. With Google maps, the researchers calculated the distance between where the women lived and their place of treatment. For rural women, the nearest radiation facility was 21.9 miles away, on average. Urban women had to travel less than 5 miles to get treatment, the findings showed. The report was published online recently in The Journal of Rural Health. “Radiation treatment is not just a one-time thing,” Longacre explained in a university news release. “Conventional radiotherapy requires treatment five days per week for five to seven weeks at a time. This means that the average rural woman logs more than 2,000 miles of travel over the course of treatment.” Longacre’s team also investigated the characteristics of […]
Latest Arthritis News FRIDAY, Feb. 21, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Taking their medications as prescribed significantly lowers lupus patients’ risk of developing diabetes, a new study finds. Type 2 diabetes is a common complication of lupus, an autoimmune disease that can cause damaging inflammation in many organs, as well as rashes, fatigue and joint pain. For the new study, researchers analyzed four years of data on nearly 1,500 lupus patients in British Columbia, Canada, and found that those who followed their medication regimen were much less likely to develop type 2 diabetes. In particular, those who consistently took antimalarial drugs like hydroxychloroquine had 39% lower odds of developing diabetes, according to the study published recently in Arthritis Care & Research. “Antimalarial drugs are actively used to treat lupus symptoms long-term,” said senior author Mary de Vera, a professor of pharmaceutical sciences at the University of British Columbia, in Vancouver. “Now we know that they can also significantly protect patients against type 2 diabetes, if taken as prescribed for the required length of time.” To reduce their risk of diabetes, lupus patients need to take their medications at least 90% of the time, according to the researchers. “It’s not enough to […]
Latest Senior Health News By Steven ReinbergHealthDay Reporter THURSDAY, Feb. 20, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Caring for a loved one at home can be rewarding, but it can also be overwhelming and take a toll on your own health, a new study suggests. According to a new report from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, nearly 1 in 5 of the nearly 18 million Americans who provide informal, unpaid care may be in fair or poor health. “As the population of America ages and the number of older adults with diseases such as Alzheimer’s continue to grow, there concomitantly has been a growth in the number of non-paid, informal caregivers,” said Dr. Teresa Murray Amato, director of geriatric emergency medicine at Long Island Jewish Forest Hills in New York City. “Many of these caregivers are family members, which can be very helpful for allowing older adults to remain at home,” said Amato, who was not part of the study. Over the three years of the study (2015 to 2017), using data from 44 states, the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico, researchers led by the CDC’s Valerie Edwards found that 21% of more than 252,000 respondents were caregivers. […]
Latest Healthy Kids News By Amy NortonHealthDay Reporter THURSDAY, Feb. 20, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Teenage actor Gaten Matarazzo III was born with a rare genetic disorder that affects bone development. And ever since his Netflix series “Stranger Things” became a hit, public interest in the condition has shot up, a new study finds. The disorder, called cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), affects only about one in a million people, according to the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Caused by a mutated gene, CCD leads to abnormal bone development — most apparent in the collarbones and teeth. The collarbones are either only partially developed or absent, causing the shoulders to slope toward each other in the front of the body. The teeth do not come in fully, and the ones that do may be misaligned or misshapen. Some other CCD effects include scoliosis, an abnormal curvature of the spine; a prominent forehead; and larger-than-normal spaces between the skull bones that may fail to close during childhood — as they usually would. Not only does Matarazzo live with CCD, so does his “Stranger Things” character, Dustin Henderson. And since its debut in 2016, the series has featured scenes with Dustin educating others about […]
Latest Infectious Disease News FRIDAY, Feb. 21, 2020 (HealthDay News) — The number of coronavirus cases among Americans jumped to 34 Friday, as U.S. health officials reported that more passengers who were evacuated from a quarantined cruise ship in Japan have tested positive for the virus. “We have 13 U.S. cases, versus 21 cases among people who were repatriated,” Dr. Nancy Messonnier, director of the U.S. National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said during a media briefing Friday. “The repatriated cases include 18 passengers from the Diamond Princess [cruise ship] and three from the Wuhan repatriation flights.” However, nearly everyone evacuated in the special flights from Wuhan have finished their 14-day quarantine, Messonnier added. Of the Diamond Princess patients who are now in the United States, 11 are receiving care at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, five are receiving care around Travis Air Force Base in northern California and two are being cared for around Lackland Air Force Base in Texas, Messonnier said. “Because the passengers on the Diamond Princess were in a close setting where there has been a significant spread of COVID-19, they are considered at high risk for infection and we do expect to see […]
Latest Infectious Disease News By Peter Schelden on 02/21/2020 3:43 PM Source: MedicineNet Health News As the global death toll tops 2,100, COVID-19 infections continue to spread in countries across the world, including in the U.S. The region with the most infections is the West Coast, with 11 confirmed cases out of 15 total. In comparison, the East Coast has confirmed only one case. There are nine confirmed COVID-19 cases in California, including one patient recently evacuated from the Diamond Princess cruise ship in Japan. Another case was reported last week in Arizona involving a man in his 20s, according to The Arizona Republic. The first confirmed case in the U.S. appeared in Washington state. Other people have tested positive elsewhere in the US. Two cases have been confirmed in Illinois, one in Wisconsin, and one in Texas. The only East Coast state with any confirmed COVID-19 cases is Massachusetts, which reported a Boston man in his 20s was infected earlier this month. An additional 13 evacuees from the Diamond Princess were taken Monday to health facilities in Omaha. These patients are in quarantine. The CDC does not reflect these cases in its official statistics, but confirmed in a statement […]
Latest Infectious Disease News Brenda GoodmanFebruary 20, 2020 As countries work to slow the spread of the virus that causes COVID-19, the screening of international travelers has become a cornerstone of those efforts. Because there are a limited number of lab tests, travelers generally aren’t being swabbed unless they have symptoms or if they’ve answered yes to certain questions. They include whether the travelers recently had close contact with someone who has tested positive for the virus, which is now officially called SARS-CoV-2. A new study by German researchers shows why that approach probably isn’t catching everyone who’s infected. The researchers tested 126 people who were returning to Germany after recent travel from China. On the flight, 10 people were isolated because they were at high risk of being infected — some had symptoms, and others had contact with people who were infected. As soon as the plane touched down, these 10 passengers were taken to a hospital and tested for the virus. None were positive. Doctors examined the rest of the passengers at a medical assessment center at the airport. One passenger had a fever, a hard time breathing, and a cough. He was also tested, and was negative […]
Latest Infectious Disease News FRIDAY, Feb. 21, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Eleven Americans who were evacuated from a quarantined cruise ship in Japan have tested definitively for coronavirus, bringing the case count in this country to 26, U.S. health officials reported late Thursday. In China, the number of new cases of COVID-19 continued to decline on Friday, but South Korean officials battled to contain the rapidly spreading virus in its country. The first case was reported on Tuesday in that country; by Friday, that number had climbed to 204, the AP reported. The decline in Chinese cases has been due in part to Chinese health officials changing how they tally infections. Under the new system, there have now been a total of 75,465 cases and 2,236 deaths in mainland China. Among the 400 Americans who were on board the Diamond Princess cruise ship, roughly 300 Americans were evacuated over the weekend and are under quarantine in the United States. The 11 passengers whose tests came back positive for coronavirus were part of a group of 13 high-risk passengers who had been at Travis Air Force base in northern California since the cruise ship evacuation, the AP reported. They have since […]
Latest High Blood Pressure News THURSDAY, Feb. 20, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Millions of Americans with high blood pressure are at risk of heart attack and stroke, but just a few changes might cut that risk. “In February, American Heart Month, we encourage all Americans to take control of their heart health by better understanding and monitoring their blood pressure levels and making healthy lifestyle changes that can significantly reduce their risk of serious health consequences associated with high blood pressure,” said Dr. Patrice Harris, president of the American Medical Association (AMA). “High blood pressure is the nation’s leading risk factor for heart attack and stroke, yet an overwhelming number of U.S. adults are living with uncontrolled high blood pressure,” Harris said in an association news release. In honor of American Heart Month, the AMA provided six tips for improving heart health: Know your blood pressure. Understand what your numbers mean and how you can get your blood pressure under control. Follow a treatment plan to manage your high blood pressure. Work with your doctor and commit to realistic lifestyle changes. Get active. Healthy adults from ages 18 to 65 should get 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity per week. Eat […]
Latest Heart News THURSDAY, Feb. 20, 2020 (HealthDay News) — For decades, artery-opening stents have helped prevent heart attacks, and new research suggests they might also help prevent strokes in the brain. In a new study, the self-expanding, intracranial Wingspan brain stent seems effective over the long term in reducing stroke patients’ risk of a subsequent stroke and death. Intracranial stents are tiny mesh tubes that are permanently implanted to open clogged brain arteries and improve blood flow to the brain. The new study looked at medical registry data on recurrent stroke or death in more than 150 stroke survivors who’d received a Wingspan brain stent. The stent appeared to cut risks in half, said American Heart Association (AHA) president-elect Dr. Mitchell Elkind. “After a year, there was a low risk of recurrent stroke or death in these patients compared to what we would expect historically,” Elkind said. “So, about 9% or so of the patients had a recurrent event, compared with what we would expect to be closer to about 20%.” He stressed that this study wasn’t a “gold-standard” randomized clinical trial. Still, “this is promising, and it suggests that for some patients, the benefits of stenting may be […]
Latest Heart News By Serena GordonHealthDay Reporter THURSDAY, Feb. 20, 2020 (HealthDay News) — A noninvasive magnetic brain stimulation device worn less than an hour a day can increase activity near stroke-injured areas of the brain, a small, preliminary study suggests. Those improvements in brain activity might then lead to increased motor function in people who have had a stroke, the researchers said. “We were excited to see a strong hint of improved motor function even in this small study. There is hope for stroke survivors with chronic motor impairment,” said study senior author Dr. David Chiu, director of Houston Methodist Hospital’s Eddy Scurlock Stroke Center. The study included 30 ischemic stroke survivors. An ischemic stroke is one in which a blood vessel becomes blocked, preventing blood flow to the brain. If blood flow isn’t quickly restored, brain damage occurs. The study volunteers all had some brain damage, and as result, had weakness on one side of their body. Chiu said researchers chose people who were at least three months post-stroke because spontaneous improvements generally don’t happen after that. That means any improvements seen could be attributed to the device. The device, which is controlled with a smartphone, looks like […]
Latest Heart News THURSDAY, Feb. 20, 2020 (American Heart Association News) — On Feb. 20, 1962, John Glenn made history when he became the first American to orbit the Earth. About half an hour after launch, somewhere over Zanzibar, he made a bit of lesser-known history by becoming the first person to use workout equipment in space. “It was called the MA-6 In-flight Exercise Device,” said fellow space veteran James A. Pawelczyk, associate professor of physiology and kinesiology at Pennsylvania State University in University Park. “And it was basically a strap connected to a bungee cord and a handle.” Glenn put his feet through the strap and worked out, while his pulse and blood pressure were measured. That might seem like a minor footnote to a grand adventure. But it shows that from the days of Glenn’s first, short flight, we’ve been asking, “How does the cardiovascular system adapt? And can we keep it healthy?” said Pawelczyk. The answer to that second question offers lessons to those of us who may never get closer to space than an episode of “Star Trek.” In short, no matter where you are, if you want to live long and prosper, you should stay […]
Latest HIV News THURSDAY, Feb. 20, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Adults with HIV have higher rates of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and are diagnosed with the lung disease years earlier than those without HIV, a new study finds. Smoking may be a major reason why, researchers suggest. “As people with HIV live longer, it is important to understand how common other illnesses are to ensure that prevention, screening and treatment strategies can be developed,” said Tony Antoniou, a scientist at the Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute of St. Michael’s Hospital, in Toronto. “While other factors may contribute to the development of COPD in people with HIV, our work highlights the importance of trying to help our patients with HIV quit smoking to prevent COPD in the first place and prevent further lung damage in people who are already diagnosed with COPD,” Antoniou said in a hospital news release. For the study, the researchers analyzed COPD rates among adults aged 35 and older in the province of Ontario, Canada, between 1996 and 2015. More than 40% of Canadians with HIV live in Ontario. Compared to those without the AIDS-causing virus, people with HIV had a 34% higher rate of COPD […]
Latest Diabetes News THURSDAY, Feb. 20, 2020 (American Heart Association News) — Emerging research may help doctors devise better ways to prevent some of the tens of thousands of amputations unrelated to traumatic injury that occur in the U.S. each year. Diabetes is the leading cause of nontraumatic lower limb amputations, including of the toe and foot. That’s partly because diabetes increases risk of peripheral artery disease, or PAD, a narrowing of major blood vessels in the legs and other areas distant from the heart. But research emphasizes another problem in the mix – microvascular disease, impairment of the tiniest blood vessels, which deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissue. Microvascular disease can damage the eyes (retinopathy), the kidneys (nephropathy) and the nerves (neuropathy). Instead of viewing these as separate conditions, researchers suggest in a new review article that they be considered a potential systemic, or body-wide, dysfunction. The article appeared Thursday in the American Heart Association journal Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. Diabetes, along with high blood pressure, can cause large blood vessels to thicken, narrowing their interior, and small vessels to shrivel or disappear, said Dr. Joshua Beckman, director of vascular medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, […]
Latest Cold and Flu News By Dennis ThompsonHealthDay Reporter FRIDAY, Feb. 21, 2020 (HealthDay News) — It’s been overshadowed by the new coronavirus outbreak in China, but this year’s flu season could be near its peak after surging throughout the United States for months. At least 14,000 people have died and 250,000 have already been hospitalized during the 2019-2020 flu season, according to estimates from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. More than 26 million Americans have fallen ill with flu-like symptoms. “There is a deadly respiratory virus that is circulating throughout the United States, and it is at its peak. It is not novel coronavirus,” said Dr. Pritish Tosh, an infectious disease specialist with the Mayo Clinic, in Rochester, Minn. This flu season has come in two waves and has been particularly hard on children, the experts said. The season started early, in October, with an unusual wave of influenza B virus. Influenza B is less likely than other strains to mutate and become more virulent. That means it poses a greater threat to young people than to older folks, who may have gained immunity because they encountered the strain before. There have been 92 flu-related deaths […]
Latest Cold and Flu News THURSDAY, Feb. 20, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Climate change, and the sudden weather changes it brings, could fuel future flu epidemics, researchers warn in a new report. They used historical data to assess how major weather swings in the fall months could affect flu season in highly populated areas of the United States, mainland China, Italy and France. Specifically, the researchers examined weather patterns and average temperatures from Jan. 1, 1997, to Feb. 28, 2018, over more than 7,700 days. They also analyzed influenza data from the four countries over the same time period. Previous research suggested that low temperatures and low humidity in the winter create favorable conditions for flu virus transmission. However, the 2017-2018 flu season was one of warmest on record, and also one of the deadliest. During the 2017-2018 flu season, extreme swings in autumn weather “kick-started” the flu, resulting in flu cases early in the season that snowballed in highly populated areas, according to the study authors. “The historical flu data from different parts of the world showed that the spread of flu epidemic has been more closely tied to rapid weather variability, implying that the lapsed human immune system […]
Latest Cold and Flu News THURSDAY, Feb. 20, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Though a severe flu season is now in full swing in the United States, a new government report delivers a bit of good news: This year’s vaccine is working well against the viruses that are circulating. “Preliminary vaccine effectiveness estimates indicate that the 2019-20 flu vaccine is providing substantial protective benefit, particularly among children, who were hard hit by flu this season,” said researchers from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “Flu vaccines are reducing doctor visits associated with flu illness by 45% overall and [by] 55% in children,” the new report stated. What does that portend for the rest of the season? Similar preliminary estimates in other flu seasons translated into overall effectiveness that ranged between 40% and 60%, according to the report published Feb. 21 in the CDC publication Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Because of the apparent success of this season’s vaccine, the CDC continues to recommend that anyone aged 6 months or older still get vaccinated if they haven’t already, “because influenza activity is ongoing, and the vaccine can still prevent illness, hospitalization, and death,” the report said. This flu season has […]
Latest Alzheimer’s News FRIDAY, Feb. 21, 2020 (HealthDay News) — A proposed project to map the genes of 1 million people in New York living with or at-risk for Alzheimer’s disease was announced Friday by Gov. Andrew Cuomo. He said the five years of data collected by the Curing Alzheimer’s Health Consortium initiative at the State University of New York would help researchers working to slow the progression of Alzheimer’s, the Associated Press reported. The state will seek proposals for private providers to work with SUNY, other hospitals and non-profit higher education research institutions on the project, Cuomo said. There is no cure for Alzheimer’s disease, which affects more than 5 million people in the United States. Current drugs only temporarily reduce symptoms, the AP reported. Copyright © 2019 HealthDay. All rights reserved. QUESTION One of the first symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease is __________________. See Answer
Latest Prevention & Wellness News WEDNESDAY, Feb. 19, 2020 (HealthDay News) — The mystery of “stinging water” has been solved, scientists say. Stinging water is the seawater near and around upside-down jellyfish (Cassiopea) — and swimmers can get stinging, itchy skin while submerged in it, even if they have no direct contact with the creatures themselves. But it wasn’t clear in the past if the jellyfish were to blame for this discomfort, since several other possible causes had been suggested, including severed jellyfish tentacles, “sea lice,” anemones and other stinging marine animals. In this new study, researchers concluded that stinging water is caused by toxin-filled mucus that the jellyfish release into the water. The mucus contains gyrating balls of stinging cells called cassiosomes. “This discovery was both a surprise and a long-awaited resolution to the mystery of stinging water,” said study author Cheryl Ames, a research associate at the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History in Washington, D.C., and an associate professor at Tohoku University in Japan. “We can now let swimmers know that stinging water is caused by upside-down jellyfish, despite their general reputation as a mild stinger,” Ames said in a Smithsonian news release. The study — by […]
Latest Pregnancy News THURSDAY, Feb. 20, 2020 (HealthDay News) — A slightly increased risk of birth defects was found among women who took macrolide antibiotics early in pregnancy, a new study shows. Researchers analyzed data from 104,605 children who were born in the U.K. between 1990 and 2016 and whose mothers were prescribed either macrolides or penicillin during pregnancy, CNN reported. The rate of major birth defects among women who took macrolides during the first three months of pregnancy was 28 per 1,000 births, compared with 18 per 1,000 births among those who took penicillin. Specifically, the risk of heart defects was higher in women who took macrolides, but they did not have a higher risk of neurodevelopmental birth defects than those who took penicillin, CNN reported. There was no increased risk of birth defects among women who took macrolides before pregnancy, according to the study published Feb. 19 in the journal BMJ. Macrolides — which include erythromycin, clarithromycin and azithromycin — are often prescribed for patients who are allergic to penicillin. They are among the most widely used antibiotics in Western countries, the researchers noted. Based on the findings, pregnant women and their doctors should consider using alternatives to […]
Latest Pregnancy News WEDNESDAY, Feb. 19, 2020 (HealthDay News) — In what doctors call a breakthrough, a cancer patient in France gave birth to the first baby conceived from an immature egg that was matured in the laboratory, frozen, then later thawed and fertilized. “We were delighted that the patient became pregnant without any difficulty and successfully delivered a healthy baby at term,” said team leader Michaël Grynberg, head of reproductive medicine and fertility preservation at Antoine Béclère University Hospital, near Paris. Loss of fertility is always a potential hazard after chemotherapy and radiation treatments for younger female cancer patients. In such cases, doctors typically induce “ovarian stimulation” to produce and harvest mature eggs from ovaries so that they can be frozen for potential future use. “However, for some patients, ovarian stimulation isn’t feasible due to the need for urgent cancer treatment or some other contraindication,” Grynberg said in a news release from the journal Annals of Oncology, which published the report Feb. 19. The French team hoped that in these cases, a technique called in vitro maturation (IVM), where the egg maturation process is induced in the laboratory, might work. “My team and I trusted that IVM could work […]
Latest Neurology News By Serena GordonHealthDay Reporter THURSDAY, Feb. 20, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Love to cross-country ski? Well, all those days spent striding across the snow-covered wilderness may do more than keep you in great physical shape. Swedish researchers report that very fit long-distance skiers were about 30% less likely to develop Parkinson’s disease during their 20-year study. The research suggests that any activity that keeps you fit might buffer the brain against disease. “Our study highlights the importance of staying physically active throughout life, in order to have a reserve to better cope when the frailties and diseases of old age inevitably arrive,” said study senior author Tomas Deierborg. He’s an associate professor in neuroscience at Lund University in Sweden. Deierborg said the researchers believe these very fit athletes have built up a greater “motor reserve” that slows any brain damage from Parkinson’s disease. He said it’s similar to the idea of “cognitive reserve” in people with dementia that suggests someone who is well-educated can sustain more brain damage from dementia before symptoms of the disorder become obvious. However, not everyone is convinced that motor reserve is playing a role in this study’s findings. Dr. Michael Okun, national […]
Latest Neurology News By Dennis ThompsonHealthDay Reporter WEDNESDAY, Feb. 19, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Rising drug costs are hampering the care of patients with debilitating neurological disorders like Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s, a new study finds. Patients are less likely to fill necessary prescriptions as out-of-pocket costs increase, said senior researcher Dr. Brian Callaghan, a neurologist with the University of Michigan, in Ann Arbor. “It’s a pretty predictable 5% to 10% drop for every $50 increase in cost,” Callaghan said. For patients with Parkinson’s disease, not taking medications as prescribed can severely impact their quality of life, he noted. “The Parkinson’s medicines are supposed to help make their tremors better, help them walk faster better. Theoretically, it could prevent falls and hospitalizations,” Callaghan said. “It’s not really preventing people from dying. It’s enabling people to live better and have better symptom control.” Previous studies have shown that out-of-pocket drug costs are rising for neurologic medications, Callaghan said. To see how these higher prices affect patient care, Callaghan and his colleagues singled out three neurologic diseases for which there are effective drugs available at a wide variety of prices: The researchers used a private insurance claims database to track more than […]
Latest Neurology News By Alan MozesHealthDay Reporter WEDNESDAY, Feb. 19, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Young boys whose mothers were exposed to chemicals known as phthalates while pregnant may face an increased risk for developing behaviors associated with autism, a new study warns. Phthalates are chemicals found in many household products, including cosmetics and plastics. The study didn’t identify a heightened risk for autism per se among boys, but rather a “small” increase in the chance for developing certain autism-related traits by age 3 or 4. These include social impairment, repetitive behaviors and restricted interests, said study lead author Youssef Oulhote. This elevated risk was not seen in girls. But it appears that folic acid supplements while pregnant offer protection against this risk, said Oulhote, an assistant professor of biostatistics and epidemiology at the University of Massachusetts Amherst. “The main finding of this study is not just that phthalates are associated with more autistic traits, but mainly how adequate folic acid supplementation in pregnancy may offset these effects and protect from potential harmful chemicals. This is an important finding,” he added. Phthalates have long been the subject of controversy. Research has suggested they could disrupt hormones in developing children. Despite their […]
Latest Infectious Disease News THURSDAY, Feb. 20, 2020 (HealthDay News) — The number of new COVID-19 coronavirus cases in China dropped Thursday, but the decline might just be due to new methods in how case numbers are tallied. Also on Thursday, two infected passengers from the Diamond Princess cruise ship that had been quarantined in Japan died. The decline in Chinese cases was due in part to Chinese health officials again changing how they tally infections. Now, they are discounting patients whose lab tests come back negative and they are refining how they first assess sick patients, the Associated Press reported. Under the new system, 394 new cases of COVID-19 were confirmed Thursday while 279 were discounted, the wire service said. There have now been a total of 74,576 cases and 2,118 deaths in mainland China. The two cruise ship passengers who died were an elderly Japanese couple who had been hospitalized during the quarantine, the AP reported. The ship’s quarantine ended Wednesday. Among the 400 Americans who were on board that same cruise ship, roughly 300 Americans were evacuated over the weekend and are under quarantine in the United States. At least 14 of those evacuees have tested positive […]
Latest Heart News By Amy NortonHealthDay Reporter WEDNESDAY, Feb. 19, 2020 (HealthDay News) — There may be something about a patient’s age of 80 that makes doctors alter their heart attack treatment decisions — consciously or not, new research suggests. In a study of U.S. heart attack patients, researchers found that just one month in age made a difference in whether doctors performed bypass surgery — one of the treatments for the artery blockages that cause heart attacks. Among patients who had turned 80 within the past two weeks, just over 5% received bypass surgery. In contrast, the rate was 7% among patients who were about to turn 80 in the next couple weeks. Researchers said the finding points to a “left-digit bias” — where doctors may be more concerned about surgery complications just because a patient’s age starts with an 8 rather than a 7. “These patients were really all the same age, with just a few weeks separating them,” said lead researcher Dr. Anupam Jena, an associate professor at Harvard Medical School. “But this study suggests doctors were seeing them differently.” Coronary bypass surgery involves taking a healthy blood vessel from a patient’s leg, arm or chest, and […]
Latest Heart News WEDNESDAY, Feb. 19, 2020 (HealthDay News) — An expandable artificial heart valve could save children with congenital heart disease from repeated open heart surgeries as they grow up, researchers report. Current artificial heart valves are fixed in size, meaning children need to get larger ones as they grow. Children who receive their first artificial valve before age 2 will require up to five open-heart operations before they become adults. This new design means children could keep the same artificial heart valve until adulthood, and it could also benefit adults with heart valve defects, according to the Boston Children’s Hospital team. Current artificial heart valves have three leaflets, tiny flaps that provide a one-way inlet or outlet for blood to keep it flowing in the right direction. This new valve has two leaflets and as a patient grows it can be expanded through a minimally invasive balloon catheter procedure. Lab tests, computer simulations and extensive testing in animals show that the new artificial valve works across a wide range of sizes, and remains functional when expanded, according to a study published online Feb. 19 in the journal Science Translational Medicine. “We hope to bring this new device into […]
Latest Heart News WEDNESDAY, Feb. 19, 2020 (American Heart Association News) — The highs and lows of the daily weather could signal something more important than which outfit to wear: A study from South Korea suggests the more temperatures fluctuate during the summer, the more severe strokes become. Connections between the weather and risk of stroke have been examined for years. To expand on that, researchers at Seoul National University Hospital focused on the effect of diurnal temperature range – that’s the difference between the day’s high and low – and the severity of ischemic stroke, the most common kind. Researchers analyzed data from 9,249 patients in a hospital-based nationwide stroke registry. The seriousness of their strokes was compared with weather information gathered during the summers of 2016, 2017 and 2018. For every 9-degree Fahrenheit increase in average temperature range over three days, the severity of strokes increased by about 67%. And for every 9-degree increase in the temperature range on the day of a person’s stroke, the severity increased about 9%. The more days of temperature fluctuations, the more the severity appeared to increase. The preliminary research was presented Wednesday at the American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference in […]
Latest Heart News WEDNESDAY, Feb. 19, 2020 (American Heart Association News) — Red dresses and pink ribbons have helped millions of Americans become aware of the separate tolls heart disease and breast cancer take on women. But not everyone is aware of how the illnesses can intersect. Heart disease – the No. 1 killer of women – can sometimes be a complication of breast cancer treatment. Older women who survive breast cancer are more likely to die of heart disease than a cancer recurrence. Dr. Laxmi Mehta, who led the writing of a wide-ranging 2018 report from the American Heart Association on the two diseases, said the overlap exists on a spectrum. Sometimes, cancer directly causes heart problems, such as when it causes fluid buildup around the heart. Much of the time, though, the problem comes from treatments targeting cancer. Radiation therapy for breast cancer can lead to blocked heart arteries, heart valve issues and abnormal heart rhythms in some patients, Mehta said. She is professor of cardiovascular medicine and director of preventive cardiology and women’s cardiovascular health at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus. Chemotherapy and other cancer treatments can weaken the heart and lead to […]
Latest Exercise & Fitness News WEDNESDAY, Feb. 19, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Changing up the amount of weight they lift could help weightlifters get stronger with less effort, a new study suggests. In traditional weight training — called one rep max — the maximum weight an athlete can lift dictates the weight load for all sessions. This study compared one rep max with an approach called load velocity profile, in which athletes lift varying weights from session to session. Over six weeks, athletes who used the load velocity profile became stronger than those who used one rep max, despite lifting less overall, according to sports scientists at the University of Lincoln, in the U.K. The study, published recently in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research included 16 men, ages 18 to 29, with at least two years’ weight training experience. The authors said their findings could help improve lifters’ muscle strength and power and make it easier to manage fatigue during training. “There are a lot of factors which can contribute to an athlete’s performance on a particular day, such as how much sleep they have had, nutrition or motivational factors, but with traditional percentage-based methods we would have […]
Latest Diet & Weight Management News WEDNESDAY, Feb. 19, 2020 (HealthDay News) — The so-called Mediterranean diet is already considered one of the healthiest for your heart, and now scientists say it may give your gut bacteria a boost, too. The diet is typically high in fruits, vegetables, nuts, beans, olive oil and fish, and low in red meat and saturated fats. The new study finds that older adults who eat a Mediterranean diet tend to have more types of gut bacteria linked with healthy aging. One nutritionist wasn’t surprised, and believes that the diet‘s reliance on vegetables could be key to the effect. “Dark green leafy vegetables, nuts and seeds all have multifold benefits in enhancing our gut microbiome,” said Sharon Zarabi, a registered dietitian who directs the bariatric program at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York City. She wasn’t involved in the new research, which was led by Dr. Paul O’Toole, a microbiologist at University College Cork, in Ireland. According to O’Toole’s team, prior research has suggested that a poor diet can have a negative impact on an older person’s strength and stamina, as well as their microbiome — the trillions of bacteria living in the human digestive […]
What is the life expectancy after a bone marrow transplant? Pictured is an illustration of a healthy bone marrow cell — the kind doctors harvest from donors to use in bone marrow transplantation. The life expectancy, survival rate and quality of life after a bone marrow transplant have improved considerably with more accurate genetic matching with donors, following up transplantation with an antibiotic regimen to control infections, and improved post-transplant care, in general. Cancer and other diseases of the blood and bone marrow, which is responsible for manufacturing blood cells, may require a bone marrow transplant from a healthy, genetically compatible donor. Ideally, the donor marrow replaces diseased cells to allow the body to maintain healthy levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. How long can you live after a bone marrow transplant? Understandably, transplants for patients with nonmalignant diseases have a much better success rate with 70% to 90 % survival with a matched sibling donor and 36% to 65% with unrelated donors. The survival rates after transplant for patients with acute leukemia in remission are 55% to 68% with related donors and 26% to 50% if the donor is unrelated. Transplanting the patient’s own bone […]
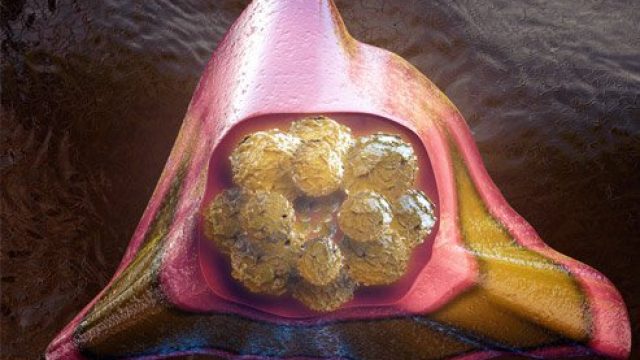
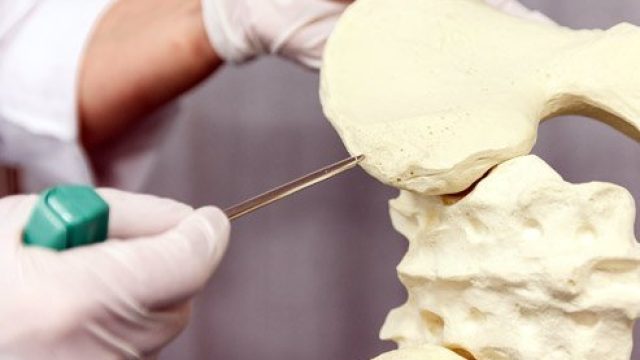
What is a bone marrow transplant? Doctors use special tools to extract bone marrow for bone marrow transplantation. Bone marrow consists of the cells that populate the internal space of your bones. The marrow manufactures three types of blood cells – red blood cells that transport oxygen, platelets that help your blood clot, and white blood cells that fight off infection. Diseases of the marrow and blood can be debilitating or fatal, but for certain diseases, a treatment method is to implant some healthy bone marrow from a genetically compatible donor into a patient in the hope it will grow and replace the diseased marrow. Often, the patient’s own cancerous marrow is destroyed prior to restoring the patient’s marrow with the new healthy donor cells. Bone marrow transplantation discovery and development The fear of nuclear warfare after the World War II initiated study of radiation effects on the human body. Initial studies on animals showed radiation had some of the most damaging effects on the bone marrow, and researchers then tested bone marrow transplants on these irradiated animals. From the 1950s through 1960s, doctors performed several bone marrow transplants between genetically similar donors and leukemia patients (called “allogenic” transplants), without […]
Latest Cancer News WEDNESDAY, Feb. 19, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Gay and bisexual men in the United States have higher skin cancer rates than heterosexual men, while bisexual women have lower rates than heterosexual women, according to a new study. Researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston analyzed data culled from national surveys conducted from 2014 to 2018 and found that skin cancer rates were 8.1% among gay men, 8.4% among bisexual men, and 6.7% among heterosexual men. Rates were 4.7% among bisexual women, 5.9% among lesbian women, and 6.6% among heterosexual women. The difference in rates between lesbian women and heterosexual women was not statistically significant, according to the researchers. These findings could be important for patient education and community outreach programs to reduce skin cancer risk, the study authors said. “It’s absolutely critical that we ask about sexual orientation and gender identity in national health surveys; if we never ask the question, we’d never know that these differences exist,” said study author Dr. Arash Mostaghimi, director of dermatology inpatient service at Brigham and Women’s. “This information helps inform the nation about how to allocate health resources and how to train providers and leaders,” he said in a […]
Latest Cancer News THURSDAY, Feb. 20, 2020 (HealthDay News) — A U.K. woman played her violin during her brain tumor surgery. Dagmar Turner, 53, is a violinist with the Isle of Wight Symphony Orchestra and a number of choral societies. Before her surgery, doctors at King’s College Hospital in London mapped her brain to pinpoint areas that are active when she plays the violin and those that control language and movement, the Associated Press reported. Midway through the surgery, Turner was wakened and asked to her play her violin to “ensure the surgeons did not damage any crucial areas of the brain that controlled Dagmar’s delicate hand movements,″ according to the hospital. “We knew how important the violin is to Dagmar, so it was vital that we preserved function in the delicate areas of her brain that allowed her to play,″ Prof. Keyoumars Ashkan, Turner’s neurosurgeon, said, the AP reported. “We managed to remove over 90% of the tumor, including all the areas suspicious of aggressive activity, while retaining full function in her left hand,” Ashkan said. Turner left the hospital three days after her surgery and hopes to make a quick return to her orchestra, the AP reported. Copyright […]
Latest Arthritis News WEDNESDAY, Feb. 19, 2020 (HealthDay News) — The U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved three drugs for nonprescription, over-the-counter use — Voltaren Arthritis Pain (diclofenac sodium topical gel, 1 percent), Pataday Twice Daily Relief (olopatadine HCl ophthalmic solution/drops, 0.1 percent), and Pataday Once Daily Relief (olopatadine HCl ophthalmic solution/drops, 0.2 percent) — the agency announced Friday. All three products will now be marketed as nonprescription drugs and will no longer be available as prescription drugs. For the drugs to switch to nonprescription status, data had to demonstrate the drugs’ safety and efficacy for self-medication use as directed in proposed labeling, according to the FDA. The nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug Voltaren Arthritis Pain, previously Voltaren Gel 1 percent, was first approved in 2007 as a prescription drug indicated to relieve pain from osteoarthritis of the joints, particularly joints of the hands, knees, and feet. The FDA noted that it may take up to seven days for Voltaren Arthritis Pain to work, and patients should stop using it if their pain does not improve in seven days or they need to use the product for more than 21 days. Diclofenac may cause severe allergic reactions, especially for people allergic to […]
Latest Women’s Health News By Dennis ThompsonHealthDay Reporter TUESDAY, Feb. 18, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Most folks know that being a couch potato is bad for their health, but new research suggests that women who spend hours in their chairs and sofas might face greater risks than believed. Sitting for long periods of time can increase risk factors for heart disease and diabetes, particularly if those bouts of sitting aren’t broken up by occasionally getting up and stretching, the study found. Each additional hour of total sitting time per day is linked to a 6% increase in insulin levels and a 7% increase in insulin resistance, the study showed. Further, each additional 15 minutes of uninterrupted sitting is associated with 7% higher insulin levels and an almost 9% increase in insulin resistance. Long periods of sitting were also associated with excess weight, a wider waist and increased triglyceride levels, said senior researcher Dorothy Sears. She’s a professor of nutrition at the Arizona State University College of Health Solutions, in Phoenix. “People need to think about trying to break up their sitting time,” Sears said. “Clinicians focus on getting people to exercise, but we also need to get people to think […]
Latest Women’s Health News TUESDAY, Feb. 18, 2020 (American Heart Association News) — Women who experience domestic abuse may be more likely to develop heart disease, stroke and Type 2 diabetes, new research suggests. The British study, published this week in the Journal of the American Heart Association, sought to fill in gaps in what is known about the link between domestic abuse and cardiovascular disease – the leading cause of death in women globally. One in 4 women in the U.S. has experienced domestic abuse severe enough that it resulted in injury, the need for medical help or symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder. A 2019 Canadian study found women who experienced domestic abuse had above-average risk factors for heart disease, but comprehensive research on the topic is sparse. The new study looked at data from 18,547 women over age 18 who had experienced domestic abuse and compared them to 72,231 women of a similar age who had lifestyle risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Researchers looked to see which women developed diabetes, high blood pressure and various types of cardiovascular disease, including coronary artery disease, stroke, heart failure and peripheral vascular disease. The study found women exposed to domestic abuse […]
Latest Pregnancy News TUESDAY, Feb. 18, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Having high blood pressure in a first pregnancy quadruples a woman’s risk of heart attack or death from heart disease, a new study finds. About 2% to 8% of pregnant women with previously normal blood pressure develop a condition called preeclampsia, which includes high blood pressure that usually begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy. In this study, Rutgers University researchers analyzed heart disease in 6,360 women in New Jersey, aged 18 to 54, who were diagnosed with preeclampsia during their first pregnancy between 1999 and 2013. These women were compared to pregnant women without preeclampsia. Women with preeclampsia were four times more likely to suffer a heart attack or heart disease-related death, and more than two times more likely to die from other causes during the 15-year study period. The findings were published online recently in the Journal of Women’s Health. “Women who were diagnosed with preeclampsia tended also to have a history of chronic high blood pressure, gestational diabetes and kidney disease, and other medical conditions,” said study author Mary Downes Gastrich. She’s an associate professor at the Robert Wood Johnson Medical School and a member of the Cardiovascular […]
Latest Mental Health News TUESDAY, Feb. 18, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Could stricter safety rules for rifles and shotguns help prevent suicide? Researchers at Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore analyzed nearly 4,000 firearm suicides and found that long guns, not handguns, are more often the method of choice for youths and people in rural areas. Their analysis of Maryland data for 2003 to 2018 revealed that about 45% of children and teens used long guns such as rifles and shotguns to kill themselves, compared to 20% of seniors. “It’s concerning to see that it’s not just handguns, but long guns that are used commonly in youth suicide,” said study author Dr. Paul Nestadt, an assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences. “Many of the safety protections that we have in place around the country typically don’t apply to long guns, and the data suggest that our strategy needs to be modified.” Long guns were used in 52% of rural firearm suicides, compared to 17% in urban counties, the study found. Suicide by rifle rose 60% during hunting season, when rifles may be easier to come by. “In the midst of a suicidal impulse, a person will use what they have. […]
Latest Healthy Kids News By Amy NortonHealthDay Reporter WEDNESDAY, Feb. 19, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Many U.S. teenagers may be using their smartphones to harass, humiliate or otherwise abuse their dating partners. That’s according to a recent national survey of teens who’d been in a romantic relationship in the past year. Researchers found that 28% had been victims of “digital dating abuse” — surprisingly, with boys being targets more often than girls. While teen dating abuse has long been a problem, digital technology has opened up new ways for it to happen, according to lead researcher Sameer Hinduja, co-director of the Cyberbullying Research Center and a professor of criminology at Florida Atlantic University. Teens might send threats by text; make embarrassing posts on social media; publicly share private, sometimes sexual, pictures; or secretly look through a partner’s device to monitor him or her. The new findings, from a nationally representative survey, give a better sense of how common the problem is among U.S. teens, Hinduja said. “This helps clarify what’s going on with youth who are in romantic relationships,” he said. “Many teenagers,” Hinduja said, “really don’t know what they’re doing when it comes to building healthy relationships.” Digital dating […]
Latest Healthy Kids News TUESDAY, Feb. 18, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Being small at birth after a full-term pregnancy could leave you gasping for breath later on in life. Swedish researchers report that babies with low birth weights are more likely to have poor heart-lung (cardiorespiratory) fitness when they reach adulthood. Cardiorespiratory fitness — the ability to supply oxygen to muscles during prolonged physical activity — is key for good health and can lower the risk of disease and early death. Previous research has linked preterm delivery and related low birth weight with poorer cardiorespiratory fitness later in life. In this study, researchers at the Karolinska Institute investigated how low birth weight affects cardiorespiratory fitness in people who were born after a full-term pregnancy of 37 to 41 weeks. They followed more than 280,000 males from birth to entry in the Swedish army at 17 to 24 years of age. At that time, the men had a physical exam that included a fitness test on a stationary bicycle. Those who weighed more at birth performed significantly better on the test than those who had low birth weights. In those who were born at 40 weeks, every 450 grams (about 1 […]
Latest Infectious Disease News WEDNESDAY, Feb. 19, 2020 (HealthDay News) — There’s been a crucial move forward in efforts to develop vaccines and treatments against the new COVID-19 coronavirus, U.S. researchers say. As of Wednesday, cases of infection with the virus have topped 74,000 (the vast majority in China), including more than 2,000 deaths. Therefore, a quick path to a vaccine and effective antiviral treatment is being sought by scientists worldwide. Now, researchers from the University of Texas at Austin and the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) say they’ve created the first 3D atomic scale map of a crucial part of the virus called the spike protein. It’s this piece of viral anatomy that attaches to and infects human cells. Mapping this part of the virus is an essential step in any effort to create vaccines and antiviral drugs that would effectively fight COVID-19, according to the paper published Feb. 19 in the journal Science. The research is being led by Jason McLellan, associate professor of molecular biosciences at UT Austin. Speaking in a university news release, he said his team has spent years studying other coronaviruses, including the SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV that were behind earlier, smaller outbreaks. McLellan […]
Latest Infectious Disease News WEDNESDAY, Feb. 19, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Delta Airlines is notifying passengers who were on a Feb. 6 flight from Hawaii to Japan that a Japanese couple on the flight tested positive for novel coronavirus after they returned home. Delta Flight 611 departed Honolulu and landed in Nagoya after a flight of about 10 hours, CNN reported. “We are proactively reaching out to customers who were onboard that flight as well as taking the necessary steps to ensure the safety of our customers and crew,” Delta said Monday. Hawaiian officials have been tracking the couple’s activities in Hawaii and are trying to identify people who may have had close contact with the man and woman, CNN reported. They were on Maui from January 28 to February 3, and on Oahu from February 3 until their Delta flight home, according to Hawaiian health officials. Last Friday — eight days after the couple left Hawaii — Hawaiian health officials said that the man had tested positive for coronavirus in Japan and was being treated at a hospital there, CNN reported. On the weekend, the Japan Times reported that the man’s wife had also been diagnosed with coronavirus. People […]
Latest Infectious Disease News WEDNESDAY, Feb. 19, 2020 (HealthDay News) — As the number of coronavirus cases reached 75,000 and deaths topped 2,000, a two-week quarantine of a cruise ship docked in Japan ended Wednesday. About 300 Americans were recently evacuated from the Diamond Princess over the weekend and are already under quarantine in the United States. Fourteen of those evacuees have tested positive for the new COVID-19 virus. More than 100 American passengers still remain in Japan, however, and U.S. health officials announced Tuesday that they will not be allowed to return home for at least two more weeks. According to a statement from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, containment measures that were taken on the ship “may not have been sufficient to prevent transmission. [The] CDC believes the rate of new infections on board, especially among those without symptoms, represents an ongoing risk.” Passengers who stayed on the ship will not be allowed to return to the United States until they have been off the ship for 14 days, without any symptoms or a positive test for the virus, the agency added. The ruling also applies to Americans who are hospitalized in Japan. In some […]
Latest Infectious Disease News TUESDAY, Feb. 18, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Hepatitis, appendicitis and viral meningitis are among the serious complications that can occur when you get the measles, doctors warn in a new report. The study — which outlines cases involving three adults who developed major complications — is also a reminder of the importance of vaccination against the illness. Measles is highly contagious, but it’s also easily prevented by getting a vaccine, experts note. However, unfounded fears about vaccination have resulted in reemergence of measles as a global health problem, the authors of the new study said. Measles was once thought to be almost eliminated in the United States, but cases have been increasing as pockets of “anti-vaxxers” proliferate. In 2019, nearly 1,300 cases were reported — the most since 1992, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles can also become a serious health threat, as the three cases outlined in the new European report show. The research was led by Dr. Thelma Xerri, from the Departments of Medicine and Infectious Disease at Mater Dei Hospital in Msida, Malta. While typical symptoms include fever, cough, pink eye and an extensive rash, measles suppresses the […]
Latest High Blood Pressure News By Steven ReinbergHealthDay Reporter TUESDAY, Feb. 18, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Patients taking a common diuretic to help lower blood pressure may be better off with a similarly effective but safer one, a new study suggests. Current guidelines recommend the drug chlorthalidone (Thalitone) as the first-line diuretic. But it can have serious side effects that can be avoided with another diuretic, hydrochlorothiazide (Hydrodiuril), researchers say. “Diuretics are recognized as among the best drugs to treat hypertension, but there are no randomized studies to help decide which diuretic is best,” said lead author Dr. George Hripcsak, head of biomedical informatics at Columbia University in New York City. Hydrochlorothiazide is the world’s most-used diuretic, but chlorthalidone is gaining favor because it is longer acting and, therefore, might be more effective, Hripcsak said. Guidelines from both the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association recommend chlorthalidone for that reason. But the new study found that patients taking chlorthalidone were three times more likely than those taking hydrochlorothiazide to have dangerously low levels of potassium and other electrolyte imbalances, as well as kidney problems. Six percent of patients taking chlorthalidone had low potassium, compared with 2% of those […]
Latest Heart News TUESDAY, Feb. 18, 2020 (American Heart Association News) — One Sunday in 2016, Dwight Tschetter felt lightheaded and lost consciousness. Paramedics rushed him to the hospital. At 67, he had a stroke that paralyzed his whole body. “It was a really difficult situation,” said his son, Jason Tschetter. “We were torn on what Dad would want to do. … We watched him slip away over several days. It was a wake-up call for all of us.” Eventually, this tragic time would become a gift from father to son and grandsons. Jason, who was in his early 40s, had been experiencing headaches. After his father died, he went to his family doctor, who agreed what happened to his father warranted further testing. An MRI revealed unusual vascular structures in his head, similar to what was seen in his father after his stroke. A CT scan later identified a life-threatening aortic aneurysm. Jason, who lives in the Minneapolis area, traveled in April 2018 to the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, where cardiologist Dr. Heidi Connolly warned that he needed immediate surgery. His aorta – the main artery that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body […]
Latest Heart News TUESDAY, Feb. 18, 2020 (American Heart Association News) — Traditional stroke risk factors, such as high blood pressure, smoking and diabetes, impact people of various races and genders differently, new research shows. “The biggest thing we found was that hypertension has a bigger effect on stroke among African American men than it does on (white people) or African American women, even in young adulthood,” said lead investigator Elizabeth Aradine, a vascular neurology fellow at the University of Maryland School of Medicine in Baltimore. Aradine will present the preliminary findings Wednesday at the American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference in Los Angeles. The study of more than 2,100 adults ages 18-49 in the Baltimore-Washington, D.C., region found the proportion of stroke incidence due to high blood pressure, also called hypertension, was 45.8% for African American men, compared to 26.4% for African American women. Among their white peers, it was 17.2% for men and 19.3% for women. Among smokers, white women had the highest chance of having a stroke. The incidence of stroke attributable to smoking was 32.5% for white women, compared to 23.8% for black women, 19.7% for white men and 10.1% for black men. Diabetes had a […]
Latest Cancer News TUESDAY, Feb. 18, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Many people don’t realize that cancer patients are in constant need of blood supplies. Chemotherapy and radiation treatments for cancer can damage the body’s ability to produce healthy blood cells and cause potentially life-threatening conditions. Blood transfusions help provide critical clotting factors, proteins and antibodies. Now, the American Red Cross and the American Cancer Society want to remind the public to give blood for this vulnerable group of patients. “The Give Blood to Give Time partnership is a wonderful opportunity to harness the unique strengths of both organizations and provide a way for people to help give patients and their families the resources they need to fight back,” said Gail McGovern, president and chief executive officer of the American Red Cross. “I know from experience that a loved one’s diagnosis can make family and friends feel helpless,” she added in a joint news release. “They often don’t realize that individuals can make a difference by giving blood and platelets.” Nearly a quarter of the nation’s blood supply is needed for cancer patients. “The need for blood in cancer treatments is an important and untold story,” said Gary Reedy, chief executive […]
Latest Arthritis News TUESDAY, Feb. 18, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Many Americans battling autoimmune illnesses such as rheumatoid arthritis or psoriasis turn to a long-used drug, methotrexate, for relief. But until now there’s been little comprehensive research on side effects tied to the drug. A new study funded by the U.S. National Institutes of Health may fill that gap. It finds that patients who take methotrexate do have a slight-to-moderate increased risk of certain types of side effects. “Methotrexate is a cornerstone drug for a variety of inflammatory diseases, especially for rheumatoid arthritis,” Dr. Daniel Solomon, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, said in a hospital news release. His team noted that the medicine has been in use for 40 years. To learn more about side effects, the researchers analyzed data gathered on nearly 4,800 people. All had participated in a study focused on cardiovascular inflammation, and they took either a “dummy” placebo or low-dose methotrexate combined with folate. Of the nearly 2,400 participants who took methotrexate, 87% had a notable side effect, compared with 81.5% of those who took a placebo, the study found. People who took methotrexate had small-to-moderate increases in risks for skin cancer, […]
Latest Healthy Kids News TUESDAY, Feb. 18, 2020 (HealthDay News) — A key to your baby’s asthma risk may be as close as your laundry room. Canadian research shows that an infant’s exposure to household cleaning products in the first few months of life is tied to heightened odds for asthma by age 3. Babies may be especially vulnerable because they “typically spend 80% to 90% of their time indoors, and are especially vulnerable to chemical exposures through the lungs and skin due to their higher respiration rates and regular contact with household surfaces,” according to study lead researcher Tim Takaro. He’s a physician-scientist in the faculty of health sciences at Simon Fraser University in Burnaby, British Columbia. In their research, Takaro’s group examined questionnaires completed by parents of more than 2,000 children who were exposed to household cleaning products from birth up to 4 months of age. The children were assessed at 3 years of age for asthma, recurrent wheeze and “allergic sensitization.” The study couldn’t prove cause and effect, but the researchers reported that babies with the highest levels of exposure to cleaning products had a 37% rise in their risk of being diagnosed with asthma by 3 […]
Latest Healthy Kids News By Amy NortonHealthDay Reporter TUESDAY, Feb. 18, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Little ones who stay up late may have a higher risk of becoming overweight by the time they are school-age, a new study suggests. Researchers found that young children who routinely got to sleep after 9 p.m. tended to gain more body fat between the ages of 2 and 6. Compared with kids who had earlier bedtimes, they had bigger increases in both waist size and body mass index (BMI) — an estimate of body fat based on height and weight. The findings do not prove that later bedtimes cause excess weight gain, said Dr. Nicole Glaser, who wrote a commentary accompanying the study, which was published online Feb. 18 in Pediatrics. But the report adds to evidence linking sleep habits to kids’ weight, according to Glaser, a pediatric endocrinologist at the University of California, Davis. Specifically, studies have found higher rates of obesity among kids who either get too little sleep or have trouble falling or staying asleep. “At this point, I think it’s clear that there is a relationship between [sleep quality and obesity risk],” Glaser said. “The big question is whether the […]
Latest Infectious Disease News MONDAY, Feb. 17, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Fourteen of the more than 300 U.S. passengers evacuated from a cruise ship hit by the coronavirus outbreak have tested positive for infection during their flights home, U.S. health officials said Monday. The news comes from a joint statement from the Departments of State and Health and Human Services, CNN reported. The 14 passengers aboard the Diamond Princess, docked in Yokohama, Japan, tested positive for the new COVID-19 virus during the disembarkation process, officials said. They were part of an evacuation process involving two flights back to military bases in the United States. “After consultation with HHS officials, including experts from the HHS Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response, the State Department made the decision to allow the 14 individuals, who were in isolation, separated from other passengers, and continued to be asymptomatic, to remain on the aircraft to complete the evacuation process,” the agencies said in the news release. One of the flights landed at Travis Air Force Base near Fairfield, California, around 11:28 p.m. local time Sunday, while the other arrived at Joint Base San Antonio-Lackland in San Antonio, Texas at 3:56 a.m. local […]
Latest Infectious Disease News THURSDAY, Feb. 13, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Scientists say that 90% of dengue cases could be slashed by artificially infecting mosquitoes. Dengue viruses are spread to people by infected mosquitoes. But infecting the insects with Wolbachia bacteria blocks the dengue virus from replicating in mosquitoes and being transmitted between people, the international researchers said in a new study. Wolbachia is found naturally in about 60% of insect species, including some mosquitoes, butterflies and moths. “Dengue is a leading cause of illness and death among children across the globe,” said study lead author Lorenzo Cattarino, of MRC Centre for Global Infectious Disease Analysis at Imperial College London. The team of scientists created the first worldwide map of dengue transmission intensity — a measure of how easily dengue is transmitted to people. Using this map, they predicted the effectiveness of two methods of combating dengue, vaccination and the release of mosquitoes infected with Wolbachia. In trials, scientists are infecting the mosquito species (Aedes aegypti) that carry dengue with Wolbachia and releasing them into areas where dengue is prevalent. The trials suggest the bacteria doesn’t pose a threat to animals or people. Using available data and their new transmission […]
Latest Infectious Disease News FRIDAY, Feb. 14, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Coronavirus is most infectious when patients are the peak of their illness, U.S. health officials said Friday. “Based on what we know now, we believe this virus spreads mainly from person to person among close contacts, which is defined as about six feet, through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes,” Dr. Nancy Messonnier, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said during a media briefing on Friday. “People are thought to be the most contagious when they are most symptomatic, that is when they are the sickest,” she added. “Some spread may happen by touching contaminated surfaces and then touching the eyes, nose and mouth,” she added. “But remember, we believe this virus does not last long on surfaces. Some spread may happen before people show symptoms. There have been a few reports of this with the new coronavirus, and it is compatible with what we know about other respiratory viruses, including seasonal flu. But right now, we don’t believe these last two forms of transmission are the main driver of spread.” Messonnier also noted that the U.S. Centers for Disease Control […]
Latest Infectious Disease News FRIDAY, Feb. 14, 2020 (HealthDay News) — The race is on to find effective treatments against the new COVID-19 coronavirus spreading through China, and two new therapies show real promise, researchers say. One is an experimental antiviral medicine that already being used by Chinese doctors on a “compassionate” basis in coronavirus patients and has shown effectiveness in monkey trials. The other involves transfusing the plasma of people who’ve survived COVID-19 into patients still battling the illness, in hopes of boosting the recipient’s immune defenses. The antiviral is a drug called remdesivir. It’s so new that it’s not yet approved for use by any drug regulator in the world. However, earlier this week the drug’s maker Gilead announced that remdesivir is being given to Chinese patients infected with the new coronavirus because there are no approved treatments. And in a study published Thursday in the Proceedings of the National Academies of Science, researchers found that remdesivir prevented disease in monkeys infected with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV). Good results in monkeys and people An outbreak of MERS first arose in Saudi Arabia in 2012 and caused worldwide concern before it was brought under control. Importantly, the […]
Latest Heart News THURSDAY, Feb. 13, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Optimism might be powerful medicine when recovering from a stroke, a new study suggests. Stroke survivors who had positive outlooks showed lower levels of inflammation, reduced stroke severity and fewer physical impairments after three months compared to more pessimistic stroke survivors, the researchers found. “Our results suggest that optimistic people have a better disease outcome, thus, boosting morale may be an ideal way to improve mental health and recovery after a stroke,” study first author Yun-Ju Lai said in an American Heart Association (AHA) news release. The research was funded by the U.S. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the AHA. Lai is a postdoctoral fellow in the neurology department at the University of Texas Health Science Center in Houston. The study involved a group of 49 stroke survivors. Researchers analyzed the connections between optimism, inflammation, stroke severity and physical disability. They found that as optimism increased, levels of inflammatory markers such as interlukin-6 and C-reactive protein decreased. Getting a better understanding of the relationship between these elements could help develop new strategies for stroke recovery, Lai and her colleagues said. Experiencing inflammation after a stroke can damage […]
What are bedbugs and lice? What are their main differences? Symptoms of bedbug bites include red, itchy bite marks on the face, neck, shoulders, arms, hands, and back. What are bedbugs? The common bed bug (Cimex lectularius) is considered a public health pest, but bedbugs do not transmit or spread disease. bedbugs are small, brown, oval-shaped insects that feed on blood, and their bites cause itching and irritation in humans. Bedbugs do not spread disease. Bedbugs often come into a home undetected through: Clothing Luggage Used beds and couches Other household items Usually bedbugs live in mattresses, box springs, bed frames, and headboards and bite people during the night. Bedbugs are a problem worldwide, are resurging so they may become a serious problem. What are lice? Lice are parasitic insects that feed on human blood can be found on people’s bodies. Lice found on different areas of the body differ from each other. There are three types of lice that live on humans: Pediculus humanus capitis (head louse) Pediculus humanus corporis (body louse, clothes louse) Pthirus pubis (“crab” louse, pubic louse) Body lice is the only type of lice known to spread disease. “Sea lice” is not the same as […]
Latest Neurology News FRIDAY, Feb. 14, 2020 (HealthDay News) — U.S. soldiers who suffer a moderate or severe traumatic brain injury (TBI) are more likely to suffer other mental health woes than those with other serious injuries, a new study finds. It also showed that the rate of mental health disorders among seriously injured soldiers is much higher than previously reported. “A central takeaway is that severe TBI is associated with a greater risk of mental health conditions — not just PTSD [post-traumatic stress disorder],” said lead investigator David Chin, an assistant professor of health policy and management at University of Massachusetts Amherst. “Our findings suggest that patients who are critically injured in combat and sustain severe TBIs have particularly high rates of mental health disorders,” Chin said in a university news release. He and his colleagues analyzed the records of nearly 5,000 U.S. military members — mostly from the Army or Marines — who were severely injured during combat in Iraq and Afghanistan between 2002 and 2011. Nearly a third suffered moderate or severe TBIs. Overall, 71% of the severely injured soldiers in the study were later diagnosed with at least one of five mental health conditions: post-traumatic stress […]
Latest Mental Health News THURSDAY, Feb. 13, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Ketamine use among electronic dance music party-goers is much higher than previously thought. And unintentional use appears to play a role, a new study finds. Ketamine is known as Special K on the party scene. The operating room anesthetic was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2019 as a treatment for depression. But it has long been used as a club drug. “Intentional underreporting of drug use is common, but the underreporting we found here is higher than expected, considering that many party attendees reported use of other synthetic drugs,” said lead study author Joseph Palamar. He’s an associate professor of population health at New York University in New York City. “Since it is unlikely that someone would disclose the use of drugs such as ecstasy and intentionally not report using ketamine, we believe many cases of positive detection may be due to unknown exposure through the use of adulterated drugs,” Palamar said in a university news release. For the study, researchers surveyed hundreds of adults entering electronic dance music parties in New York City about their past-year drug use. More than 200 provided hair samples […]
Latest Mental Health News By Amy NortonHealthDay Reporter THURSDAY, Feb. 13, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Young men who believe that “real men don’t cry” may be more prone to suicide, a new study suggests. It has long been known that men are more likely than women to end their own lives: In the United States, the suicide death rate among men is about 3.5 times that of women, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The statistics raise the question of whether traditional norms about masculinity could play some role, said lead researcher Daniel Coleman. On the face of it, he explained, it makes sense that those expectations of “manly” men — which include denying emotions, not reaching out for help, and aggressiveness — could contribute to suicide risk. But it’s also a challenging subject to study, said Coleman, an associate professor in the Graduate School of Social Services at Fordham University in New York City. To start to dig into it, his team used data from a health study that began tracking over 20,700 U.S. teenagers back in 1995. By 2014, 22 of them had died by suicide — all but one of whom were men. […]
Latest Healthy Kids News MONDAY, Feb. 17, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Grandparents can be a bad influence on kids’ weight, researchers say. That’s the upshot of an analysis of 23 studies conducted in the United States and eight other countries by a team from the Brown School at Washington University in St. Louis. The study found that kids who were cared for by grandparents had nearly 30% higher odds for being overweight or obese. While Grandma and Grandpa may mean well, they can affect their grandchildren’s weight in various ways, including eating habits, physical activity and perceptions of what represents a healthy lifestyle, according to the researchers. “Through offering wisdom, teaching traditions, providing guidance and making memories, grandparents are often able to leave behind a legacy that their grandchildren will cherish and benefit lifelong,” said lead author Ruopeng An, an assistant professor. “However, some negative influences from grandparental care may also be present and cannot be overlooked,” he added in a university news release. One of those negative influences affects a child’s diet and exercise habits. “The notion of ‘the bigger the healthier’ is still relevant,” An said. Some grandparents may urge their grandkids to eat bigger and more frequent […]
Latest Healthy Kids News By Alan MozesHealthDay Reporter MONDAY, Feb. 17, 2020 (HealthDay News) — More than a quarter of all opioid overdoses in the United States involve teenagers, and a full fifth of those cases were likely suicide attempts, new research shows. The findings follow an in-depth analysis of nearly 754,000 American opioid poisoning cases that occurred between 2005 and 2018. All had been reported to the U.S. National Poison Data System. And almost 208,000 of those cases involved children 18 years old or younger. During the 13-year study period, the pediatric overdose landscape has taken a turn for the worse, said study author Dr. Megan Land, a pediatric critical care fellow at Emory University’s School of Medicine in Atlanta. Most significantly, said Land, “the proportion of children with suspected suicide due to an opioid poisoning increased dramatically over our study period,” rising from just under 14% in 2005 to more than 21% by 2018. That increase, she said, “echoes findings in recent studies demonstrating that the incidence and rate of pediatric suicide attempts by [opioid] poisonings has been rising since 2011.” The study also found that during the same period, the percentage of young patients admitted to a […]
Latest Healthy Kids News SATURDAY, Feb. 15, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Sledding, skiing and ice skating are big fun in the winter, but can lead to big injuries, too. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) reminds parents to take steps to help their kids avoid injury and make sure they’re dressed appropriately for the cold weather. “This is the time of year when we see people return from winter break vacations with knee injuries from skiing, and hand or wrist injuries from snowboarding. We also see concussions from both these sports,” said Dr. Rebecca Carl of the AAP Council on Sports Medicine and Fitness. “Helmets are important for skiing and snowboarding,” Carl said in an academy news release. “Gloves with wrist guards are important for snowboarding.” The AAP offers this advice for outdoor winter play: Dress children in thin layers with a wicking layer beneath to keep kids’ skin dry. Make sure they wear a hat, gloves and boots. Set time limits for outdoor play to avoid hypothermia and frostbite. Remind children to come inside every so often to warm up. Only let your child skate on approved surfaces. Make sure they skate in the same direction as the crowd. […]
Latest Infectious Disease News New cases of the novel coronavirus continue to increase worldwide, with 73,332 confirmed global cases of COVID-19 as of today, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). That includes 72,528 cases in China and 804 cases in 25 countries outside of China. Some have questioned the accuracy of the statistics released by the Chinese government regarding the reported number of cases and deaths due to the outbreak. Now there are concerns about the accuracy of the laboratory tests used to confirm diagnoses. Reports suggest some people test negative up to six times even though they are infected with the virus, according to the BBC and Chinese media. Such was the case with Dr. Li Wenliang, the ophthalmologist who first identified the outbreak and was reprimanded by Chinese authorities when he tried to warn others. Dr. Wenliang developed a cough and fever after unknowingly treating an infected patient. He was hospitalized, testing negative for coronavirus several times before eventually receiving a positive result. On Jan. 30 the doctor posted: “Today nucleic acid testing came back with a positive result, the dust has settled, finally diagnosed,” according to the BBC. Dr. Wenliang passed away on February 7 in […]
Latest Heart News TUESDAY, Feb. 18, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Women remain underrepresented in heart disease research, even though it’s the leading cause of death among women worldwide, researchers say. Women accounted for less than 40% of all people enrolled in cardiovascular clinical trials from 2010 through 2017, according to a study published Feb. 17 in the journal Circulation. “One woman dies from cardiovascular disease every 80 seconds. It’s the leading killer of all women around the globe, claiming the lives of one in every three women, yet disparities continue to persist when it comes to symptom recognition, treatment times and methodologies, and even lifesaving support measures,” said journal editor-in-chief Dr. Joseph Hill, chief of cardiology at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas. For the study, Lijing Yan of the Global Heath Research Center at Duke Kunshan University, in China, and colleagues analyzed 740 completed cardiovascular clinical trials. Those trials were reported between 2010 and the beginning of 2018 on ClinicalTrials.gov, a U.S. government site that’s one of the largest trial registries in the world. The clinical trials included a total of nearly 863,000 adults, aged 25 to 89, with an average age of 61. Overall, only […]
Latest Heart News MONDAY, Feb. 17, 2020 (American Heart Association News) — Bleeding strokes are the deadliest type of stroke and the hardest to treat. What might make matters worse is having both diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease versus either condition alone, new research shows. The study looked at 2,071 adults in the Kentucky Appalachian Stroke Registry who had a hemorrhagic stroke. The researchers reviewed each patient’s health records to look for a previous diagnosis of diabetes or Alzheimer’s disease. They found 75% of those with both conditions had died or needed hospice or long-term care after their stroke compared to 39% with neither condition, 42% with diabetes alone, and 62% with Alzheimer’s disease alone. This stroke registry gave us “the opportunity to think about how having more than one (health condition), like diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease, could influence outcomes compared to having just one,” said the study’s lead researcher Amanda L. Trout, a scientist at the Center for Advanced Translational Stroke Science at the University of Kentucky in Lexington. Trout will present the preliminary study Wednesday at the American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference in Los Angeles. Diabetes occurs when a person’s blood sugar is too high. The condition increases […]
Latest Heart News By Serena GordonHealthDay Reporter FRIDAY, Feb. 14, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Could hot chocolate deliver relief to those suffering from the painful condition known as peripheral artery disease (PAD)? A small, new study says it’s entirely possible. Though you may be picturing a steaming cup of hot milk chocolate with tiny marshmallows bobbing on the top, the concoction the study volunteers drank was made from dark chocolate, and had a less sweet taste. “A food-derived, nutritional therapy that is accessible, inexpensive and safe may meaningfully improve walking ability in people with peripheral artery disease,” said study author Dr. Mary McDermott. She’s a professor in the departments of medicine and preventive medicine at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, in Chicago. “Peripheral artery disease is common and underdiagnosed,” she said, adding that it’s a major cause of disability in people over 55. PAD causes narrowing in the blood vessels that supply blood to the legs from the heart. Common symptoms include pain, particularly when walking, cramping and weakness in the leg muscles. McDermott noted that “these findings are particularly important because currently few therapies have been identified to help patients with PAD.” However, the study was a preliminary […]
Latest Diabetes News By Serena GordonHealthDay Reporter TUESDAY, Feb. 18, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Maybe you’ve gone to Craigslist to find a used car or a secondhand couch, but imagine having to turn to the internet to pay for lifesaving drugs. It’s already happening: A new study found that hundreds of ads were placed on Craigslist for insulin and asthma inhalers during a 12-day period in June 2019. “This study shines a light on how deeply some patients are struggling to afford lifesaving medications. Patients should not have to go to Craigslist to try to find affordable insulin and inhalers,” said study senior author Dr. Jennifer Goldstein, a research scientist with The Value Institute at ChristianaCare, in Newark, Del. People with type 1 diabetes can’t survive without a steady supply of insulin, which has to be injected. Those with type 2 diabetes who need insulin face a higher risk of serious diabetes complications if they can’t get the insulin they need. But it’s gotten increasingly harder to afford. The American Diabetes Association says the average cost of insulin in the United States nearly tripled between 2002 and 2013. The cost of asthma medications has also risen significantly in a similar […]
Latest Cancer News TUESDAY, Feb. 18, 2020 (HealthDay News) — Cases of melanoma in the United States increased 2% a year between 2005 and 2015, and will likely rise from 96,000 cases in 2019 to 151,000 cases in 2030 if the trend continues, a new study says. The researchers noted that most cases of melanoma — the deadliest type of skin cancer — in the United States are linked with ultraviolet radiation exposure from “excessive sun exposure and indoor tanning,” CNN reported. UV exposure accounted for 91% of all melanoma cases diagnosed in the United States from 2011 to 2015, and 94% of melanoma cases occurred in non-Hispanic whites, according to the study. “High indoor tanning prevalence among teen girls in the late 1990s is likely a contributing factor,” to the rising number of melanoma cases, said study author Dr. Farhad Islami, a cancer epidemiologist with the American Cancer Society, CNN reported. States with the highest UV-attributable incidence rates among all residents were: Utah, 36.3 cases per 100,000; Vermont, 31.1 per 100,000; Delaware, 28.2 per 100,000; Minnesota, 27.6 per 100,000; New Hampshire, 27.2 per 100,000; Oregon, 25.5 per 100,000; Idaho, 25.4 per 100,000; Georgia, 24.2 per 100,000; Washington, 23.9 per […]